Mazda RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Electrical Wiring Diagram
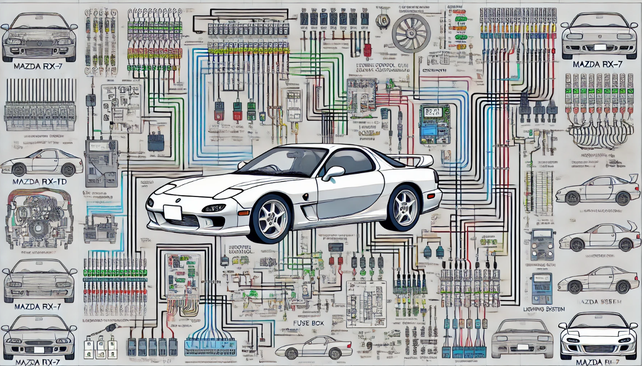
The Mazda RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Wiring diagram covers the main systems of the vehicle, including the engine control unit (ECU), ignition system, lighting, fuses and main connections. The diagram uses color-coded wires and conventional electrical symbols for ease of understanding. The diagram is designed to diagnose and repair electrical circuits, as well as to replace or upgrade components.
| Mazda RX-7 1992-2002 Engine electrical systems | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Instrument Cluster | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Warning System | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Windshield Wiper and Washer | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Rear Wiper and Washer | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Headlight Cleaner | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Exterior Lighting System | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Signal Lighting System | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Horn | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Heater and Air Conditioning | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 General Information | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Rear Window Defroster | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Interior Lighting System | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Fuse and Joint Box | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Relay | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Audio | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Theft Deterrent System | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Joint Box | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Power Window System | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Power Door Lock System | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Power Outside Mirror | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Sliding Sunroof | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Cruise Control System | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Air Bag System | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Electrical Wiring Schematic | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Common Connectors | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Ground Points | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Central Processing Unit (CPU) | Download |
| RX-7 FD 1992-2002 Switches | Download |
Mazda RX-7 FD Wiring and electrical problems
The Mazda RX-7 FD (1992-2002) has a complex electrical system, and many owners encounter a number of common wiring and electrical problems. Here are the main faults:
1. Oxidation and breakage of wiring
Over time, the insulation of the wires deteriorates, especially in the engine compartment due to high temperatures.
Contacts can oxidize, causing interruptions in the operation of systems (e.g. headlights, ignition, instrument cluster).
2. Problems with the ECU and sensors
Connections to the engine control unit (ECU) can become loose or oxidized.
Sensors (MAF, TPS, crankshaft sensor) sometimes work erratically due to poor connections.
3. Faulty relays and fuses
Blown fuses due to short circuits in the system.
Wear of the fuel pump relay, starter, cooling system.
4. Ignition problems
Broken or damaged ignition coil wires.
Poor grounding on the body, which causes a weak spark and interruptions in the engine operation.
5. Generator and battery faults
The generator may produce unstable voltage due to worn brushes or diode bridge.
A discharged or faulty battery may cause problems with starting and operating electronics.
6. Lighting and instrument panel faults
Failure of the instrument panel rheostats.
Problems with contacts in the lighting control unit.
Solutions:
✅ Regularly check the condition of the wiring, contacts and fuses.
✅ Use dielectric grease to protect contacts from oxidation.
✅ Check the weight of the car, especially in the engine compartment and on the body.
✅ If interruptions occur, diagnose the voltage in different circuits with a multimeter.
